Guidelines for Economic Evaluations - Saudi Arabia
Introduction
Economic Evaluation Studies (EES) play a crucial role in the healthcare system by providing a comparative analysis of alternative courses of action in terms of costs and consequences. The Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) has established guidelines to standardize the methods for performing, submitting, and publishing EES to ensure the safety, efficacy, and economic viability of pharmaceutical products in Saudi Arabia. This document outlines the general and specific requirements for EES submissions, with the aim of determining their added value to the current standard of practice in Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system.

Definitions
Economic Evaluation Studies (EES) involve comparing different interventions to assess their costs and outcomes. There are two main types:
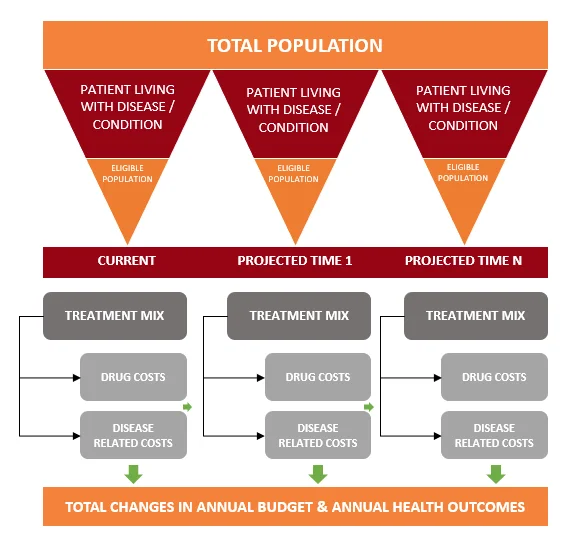
- Partial Economic Studies: Focus on either cost or consequence independently, such as Budget Impact Analysis (BIA), which evaluates the financial impact of adopting a new intervention.
- Full Economic Studies: Compare both costs and outcomes of different interventions. These include:
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis (CEA)
- Cost Minimization Analysis (CMA)
- Cost Utility Analysis (CUA)
- Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Objective
The guidance helps manufacturers and other stakeholders perform, submit, or publish EES, ensuring these studies meet SFDA standards. This ensures that new pharmaceutical products provide added value over existing treatments in Saudi Arabia.
Scope
This guidance applies to all human pharmaceutical products undergoing pricing procedures including registration, price re-evaluation, and renewal in SFDA.
General Requirements
- Epidemiological Data: Must include information on disease prevalence, incidence, and targeted population, both globally and in Saudi Arabia.
- Market Share: Data on the product’s market share in Saudi Arabia, including estimates for new products over the next five years.
- Drug Marketing Plan: Information on the targeted segment of the healthcare market in Saudi Arabia.
- Access Agreements: Details on agreements to support medicine access, such as entry agreements and patient support programs.
- List of Published EESs and HTA Decisions: Must include information on previously published EESs and summaries of HTA decisions from recognized agencies.
EES Requirements
It is mandatory to provide at least one EES for new chemical and biological products. The study options include Budget Impact Analysis (BIA), Cost Effectiveness Analysis (CEA), and Cost Utility Analysis (CUA).
Full Economic Evaluation
Full economic evaluations must include:
- Study objectives
- Targeted population
- Perspective of analysis
- Time horizon
- Comparator
- Modeling details
- Costs calculations
- Outcomes measurement
- Sensitivity analysis
- Presentation of results
Partial Economic Evaluation
Partial evaluations, such as Budget Impact Analysis, must include:
- Study objectives
- Targeted population
- Perspective of analysis
- Time horizon
- Comparator
- Sensitivity analysis
- Presentation of results
Submission Forms
All required information must be summarized in designated forms for general requirements, pharmacoeconomics, and budget impact analysis. Full studies should be attached as appendices.
Questions and Answers
An Economic Evaluation Study (EES) is a comparative analysis of different healthcare interventions in terms of their costs and outcomes. It aims to determine the added value of new interventions compared to the current standard of practice. These studies are crucial for decision-making processes in healthcare systems, as they help in assessing the financial implications and health benefits of new treatments.
There are two main types of EES:
- Partial Economic Studies: These studies focus on either the cost or the consequence of an intervention independently. An example is the Budget Impact Analysis (BIA), which evaluates the financial impact of adopting a new healthcare intervention. It helps in resource allocation by assessing the affordability of the new treatment.
- Full Economic Studies: These studies compare both costs and outcomes of different healthcare interventions. The main types of full economic studies are:
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis (CEA): Compares the relative costs and outcomes (measured in natural units) of two or more interventions.
- Cost Minimization Analysis (CMA): Assumes equivalent health effects between interventions and compares their costs.
- Cost Utility Analysis (CUA): Evaluates interventions based on cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) or other preference-based health outcomes.
- Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA): Compares both the costs and outcomes of interventions, expressing both in monetary terms.
Manufacturers, marketing authorization holders, or agents submitting human pharmaceutical products for registration, price re-evaluation, or renewal in Saudi Arabia are required to submit an EES. This ensures that the SFDA can evaluate the added value of the new products over the existing treatments in the Saudi healthcare system.
EES submissions must include comprehensive data covering several areas:
- Epidemiological Data: Information on the disease, including its prevalence, incidence, and the targeted population both globally and in Saudi Arabia.
- Market Share: Details on the current market share of the product in Saudi Arabia and estimates for new products over the next five years.
- Drug Marketing Plan: Information on the targeted segments of the healthcare market in Saudi Arabia where the product will be distributed.
- Access Agreements: Details on agreements that support the access to medicine, such as entry agreements, patient support programs, and other initiatives.
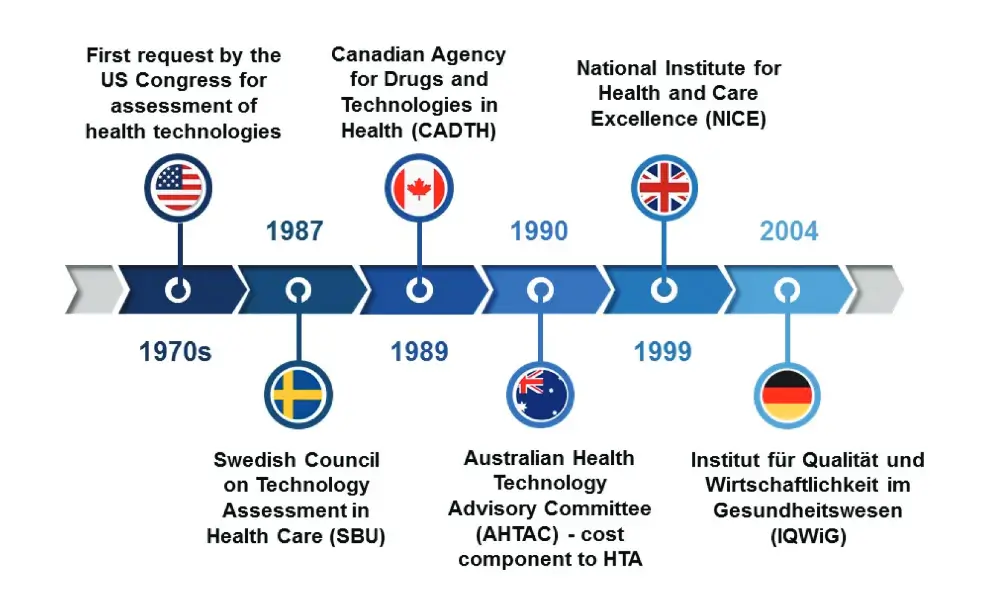
- Published EESs and HTA Decisions: Information on previously published EESs and summaries of Health Technology Assessment (HTA) decisions from recognized agencies like NICE, ICER, and CADTH.
The general requirements for an EES include:
- Epidemiological Data: Documenting the prevalence and incidence of the disease and the targeted population.
- Market Share: Providing data on the product’s market share and estimates for the future.
- Drug Marketing Plan: Outlining the plan for distributing the product in Saudi Arabia.
- Access Agreements: Detailing any agreements that facilitate access to the medicine.
- List of Published EESs and HTA Decisions: Including summaries of relevant HTA decisions and previously published EESs.
Full economic evaluations require detailed information, including:
- Study Objectives: Clearly stating the objectives and research questions.
- Targeted Population: Defining the specifications of the targeted population and including sub-group analyses.
- Perspective of Analysis: Indicating the viewpoint of the study, whether from a healthcare payer or societal perspective.
- Time Horizon: Including the natural disease history or encapsulating all cost and outcome differences over time.
- Comparator: Including the current standard of practice and emerging technologies.
- Modeling Details: Providing details and justifications for the model used, along with validation and parameterization to meet local requirements.
- Costs Calculations: Including all relevant costs, with a preference for direct healthcare costs and encouraging the inclusion of intangible costs when adopting a societal perspective.
- Outcomes Measurement: Clearly stating the effectiveness measurement, with utility measurement required for CUA.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Addressing all uncertainties through probabilistic and deterministic sensitivity analyses.
- Presentation of Results: Presenting results in cost-outcome increments, cost-effectiveness planes, and acceptability curves.
Partial economic evaluations, such as Budget Impact Analysis (BIA), must include:
- Study Objectives: Clearly stating the objectives and research questions.
- Targeted Population: Defining the specifications of the targeted population and including sub-group analyses.
- Perspective of Analysis: Indicating the healthcare payer perspective and including all cost data from Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system.
- Time Horizon: Providing a 2-5 year timeframe for the analysis.
- Comparator: Including the current standard of practice and emerging technologies.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Performing scenario analysis.
- Presentation of Results: Presenting results in table format.
- Conflicts of Interest: Reporting any conflicts of interest and funding sources.
The required forms for EES submissions are:
- Form (A) for General Requirements: Covers epidemiological data, market share, drug marketing plan, and access agreements.
- Form (B) for Pharmacoeconomics: Summarizes the pharmacoeconomics study, including study methods, population, perspective, costs, and outcomes.
- Form (C) for Budget Impact Analysis: Summarizes the budget impact analysis study, including population, comparator, costs, and results.
Any conflicts of interest and funding sources must be reported in the EES submission. Transparency in these areas is crucial to ensure the credibility and integrity of the evaluation.
Conducting EES provides several benefits:
- Informed Decision-Making: Helps healthcare policymakers and payers make informed decisions about resource allocation and the adoption of new treatments.
- Cost Management: Assists in managing healthcare costs by evaluating the financial impact of new interventions.
- Improved Patient Access: Facilitates access to effective and affordable healthcare technologies.
- Enhanced Market Access: Supports pharmaceutical companies in navigating the regulatory requirements and achieving market access for their products.
By following these guidelines and requirements, stakeholders can ensure that their EES submissions are comprehensive, accurate, and aligned with SFDA standards, ultimately contributing to better healthcare outcomes in Saudi Arabia.