World Obesity Day highlights the serious worldwide problem of increasing obesity rates and the cost of obesity, emphasising the urgent need to tackle this issue. It’s widely recognised on a global level that health issues related to obesity and related health consequences, along with their complications, significantly strain healthcare costs and reduce productivity. This places a heavy burden on society including individual morbidity, health care costs, and national economic productivity. In this article, we review the costs and value of current and future innovative healthcare to effectively address obesity and its broader societal impact.
Obesity as a Disease: An Increasing Global Health Crises
Obesity poses a significant threat to public health as it increases the risk of developing various diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hyperlipidaemia, and hypertension. Several factors contribute to the development of obesity, including genetics, environment, metabolism, lifestyle, and behavioural factors. Obesity contributes to higher death rates, as well as a decrease in quality of life and therefore, it would be highly beneficial, not just for individuals but also for society as a whole, to find effective treatment for obesity. [1]
In 2013, the American Medical Association (AMA) classified obesity as a disease requiring treatment and prevention, a decision supported by various other medical societies. This move, aimed at advancing research into the causes of obesity and enhancing treatment methods. However, the decision was controversial as the AMA’s Council on Science and Public Health had previously stated in 2012 that there was insufficient data to categorise obesity as a disease. [1] Nevertheless, obesity should be managed as a chronic disease. The most effective approach to treating obesity involves incorporating lifestyle changes and, when necessary, additional medical interventions. This strategy is implemented by a team of doctors, pharmacists, dietitians, exercise specialists, and behavioural therapists. The team should coordinate changes in dietary habits and lifestyle factors, such as promoting optimal nutrition and regular physical activity as well as possible medication. [2]
The Economic Cost of Obesity
Recent data shows a worrying increase in obesity rates worldwide over the past few decades. The World Health Organization reports that global obesity rates have tripled since 1975. Obesity doesn’t just affect individual health; it also puts a strain on healthcare systems and economies worldwide. [3] Estimates suggest that the annual cost of treating illnesses associated with obesity could range from $147 -210 billion. [1]
A recent study by Wits University found that in Africa, 9% of total healthcare spending is due to obesity-related costs. In South Africa alone, the healthcare system is losing R33 billion (US$1.9 billion) annually because of obesity, accounting for 15.38% of the government’s healthcare spending and 0.67% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The cost per person per year for dealing with overweight and obesity is around R2,769, with conditions like diabetes (R19.86 billion) and cardiovascular issues (ZAR 8.87 billion) requiring significant financial support for treatment. [4] South Africa is not alone in facing this issue; other countries with medium to high incomes, such as Brazil, South Korea, Thailand, and Colombia, are also affected. [5]
Total Economic Cost
The economic impact of obesity ranges from 1% of GDP in African countries to over 3% in countries in the Americas. By 2060, these figures are expected to rise to over 2% of GDP in African nations, more than 4% in the Americas, and exceeding 5% in Middle Eastern countries (Figure 1). Projections from 161 countries suggest that by 2060, obesity could cost 3% of global GDP. By lowering the expected occurrence of obesity by 5% yearly or maintaining 2019 values, there is an expected saving of US$430 billion or US$2.2 trillion globally from 2020 to 2060. [5]

The Role of Innovative Health Care in Obesity Management
Multiple weight-loss treatments are available for managing obesity. Research suggests that bariatric surgery is more effective at reducing weight in obese individuals compared to just changing lifestyle habits. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a newer type of minimally invasive weight-loss procedure that reduces the volume of your stomach. However, surgery comes with risks and isn’t widely accepted nationwide, leading many patients to prefer less drastic measures. [6]
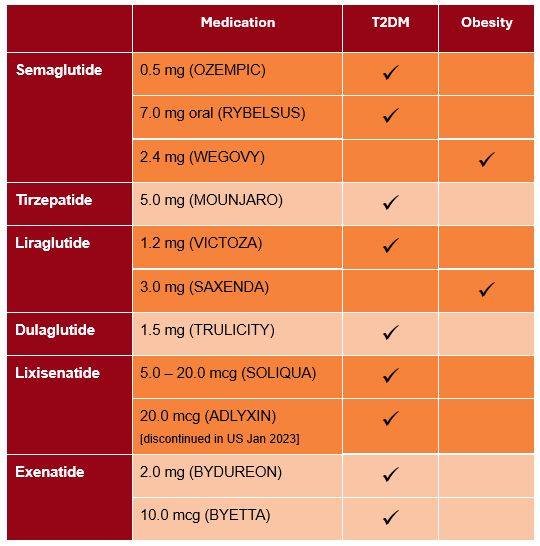
Breakthroughs in obesity medication like glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs have shown promising results in weight loss and overall health improvement. Initially approved for type 2 diabetes in 2004, it wasn’t until 2014 that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first approved a GLP-1 for obesity. Since then, these medications have become more popular and convenient as some only require weekly administration. Studies have indicated that GLP-1 treatment can lead to significant weight loss, with one recent trial demonstrating a 17% reduction in total body weight after 2 years, and the latest treatment showing a remarkable 26.6% weight loss over 84 weeks. [3][6]
Table 1. GLP-1 medications approved for use in the US.
The Cost of Obesity Treatment
We understand how important it is to make progress in treating obesity, but there are still many challenges to overcome.
Firstly, it’s essential to remember that solving obesity isn’t just about surgery and medication; people also need to make healthy lifestyle changes. Doctors have noticed that GLP-1 medications are being used more frequently, but it’s crucial to emphasise a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, and behavioural therapy. [3] These methods are better for long-term health. Secondly, there’s been pressure on the supply chain to meet the demand for effective treatments.
Thirdly, we must keep an eye on the potential long-term effects of these new treatments since we lack extensive monitoring data. It’s important not to overlook the value of lifestyle changes amidst the excitement for new treatments. [3] Lastly, the cost of these treatments is vital to ensure they can be used effectively. Research suggests that ESG is most cost-effective for a specific type of obesity, and a particular GLP-1 drug may only be cost-effective if its price is reduced. [8] Several cost analysis studies have showed that GLP-1 treatments are some of the costliest prescriptions issued in pharmacies. [3]
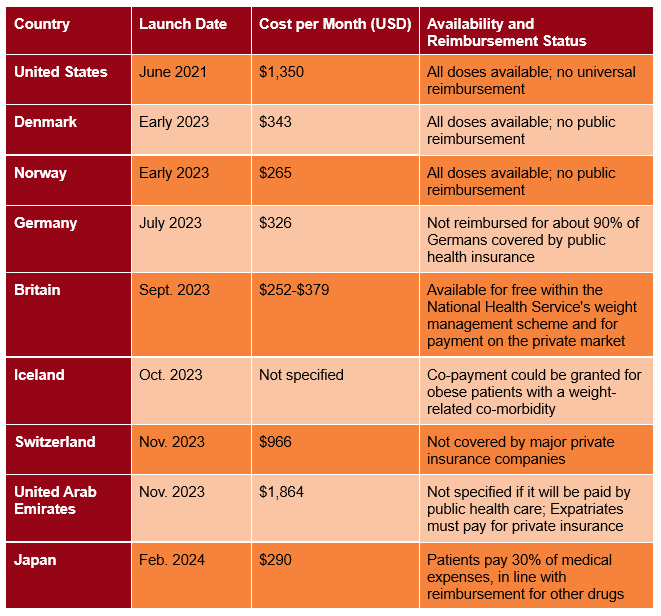
The University of Texas health system and the state of North Carolina’s health plan have decided to stop covering weight-loss medications due to their high costs as they saw a rise in cost for GLP-1 treatments from $1.5 million per month to more than $5 million per month as of May 2023. [3] The price of GLP-1 drugs differs significantly from country to country, for example, Wegovy (a GLP-1 treatment approved for obesity) has an average U.S. list price of $1,350, more than four times higher than Germany’s $326 list price. [9] Improving market transparency for GLP-1 drugs will improve access, particularly through initiatives such as direct price negotiation or the EURIPID database on medicine prices.
Table 2. Reimbursement and pricing of Wegovy in different countries.
Strategies for Accelerating Access to Healthcare Innovation
Efforts to speed up access to new healthcare solutions for managing obesity involve various approaches like changing policies, putting more money into it, and encouraging partnerships between public and private sectors. Using these new medicines or treatments could bring advantages for society, like making life better and possibly cutting down on the costs linked to diabetes and heart disease treatments in hospitals. If these drugs are covered more widely, it could save money by stopping problems caused by untreated obesity.
Even though some patients are getting better with these medicines, the high prices set by the drug companies are stopping the expected savings. Some initiatives have been launched to try and overcome the difficulty with access to effective treatment. Eli Lilly, for example, has launched LillyDirect, a website that provides resources for managing diseases and delivers certain medicines directly to people’s homes. This service is designed to help people dealing with obesity, migraines, and type 2 diabetes. [3]
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in managing obesity is still in its early phases, but its potential is significant as a means to predict and prevent obesity. This serves as another option to assist with helping to manage obesity. By pinpointing risk factors, AI can create tailored strategies to combat obesity. For instance, by using machine learning, AI can calculate the likelihood of an individual becoming overweight or obese within specific age brackets. Moreover, AI can be instrumental to monitor obesity with sensors and smartphone apps, or anticipate risks and outcomes linked to obesity. [10]
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global issue of obesity demands immediate attention and concerted efforts to address its impact on public health and economies worldwide. Obesity not only increases the risk of various diseases but also places a substantial financial burden on healthcare systems and governments. Strategies to combat obesity must involve a multi-faceted approach, including lifestyle changes, innovative treatments like GLP-1 medications, and potential advancements in AI applications.
While advancements in obesity treatment offer promising solutions, it is crucial to ensure widespread access to these innovations. Balancing the benefits of new medications with the importance of healthy lifestyle changes remains paramount. Challenges such as cost, supply chain demands, and long-term monitoring need to be carefully navigated to maximize the effectiveness of obesity management strategies.
Efforts to accelerate access to healthcare innovations for obesity management require collaborative initiatives, policy changes, and investment in public-private partnerships. By expanding access to effective treatments, society can benefit from improved health outcomes and potential cost savings in managing obesity-related conditions like diabetes and heart disease. Embracing new technologies like AI holds promise in predicting and preventing obesity, offering tailored strategies to combat this escalating global health crisis.
References:
- Rosen H. Is Obesity A Disease or A Behavior Abnormality? Did the AMA Get It Right? Mo Med. 2014 Mar-Apr;111(2):104-108. PMID: 30323513; PMCID: PMC6179496.
- Rippe JM, Crossley S, Ringer R. Obesity as a chronic disease: modern medical and lifestyle management. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998 Oct;98(10 Suppl 2):S9-15. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8223(98)00704-4. PMID: 9787730.
- ISPOR | International Society For Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research [Internet]. [cited 2 Mar 2024]. Measuring the Promise of Obesity Drugs. Available from: https://www.ispor.org/publications/journals/value-outcomes-spotlight/vos-archives/issue/view/growing-rates-of-obesity/measuring-the-promise-of-obesity-drugs
- Boachie MK, Thsehla E, Immurana M, Kohli-Lynch C, Hofman KJ. Estimating the healthcare cost of overweight and obesity in South Africa. Glob Health Action. 2022 Dec 31;15(1):2045092.
- World Obesity Federation Global Obesity Observatory [Internet]. [cited 27 Feb 2024]. Economic impact of overweight and obesity. Available from: https://data.worldobesity.org/economic-impact-new/#ZA
- Medscape [Internet]. [cited 26 Feb 2024]. Ozempic Is Appealing, but Not Cost-Effective, for Obesity. Available from: https://www.medscape.com/s/viewarticle/ozempic-appealing-not-cost-effective-obesity-treatment-2024a10001ey
- Rodriguez PJ, Cartwright BMG, Gratzl S, Brar R, Stucky N. Patients with Overweight or Obesity in the United States. [Internet]. [cited 28 Feb 2024] Available from: https://www.ispor.org/docs/default-source/euro2023/isporeurope23cartwrighthsd30poster132366-pdf.pdf?sfvrsn=af33722b_0
- Saumoy M, Gandhi D, Buller S, Patel S, Schneider Y, Cote G, Kochman ML, Thiruvengadam NR, Sharaiha RZ. Cost-effectiveness of endoscopic, surgical and pharmacological obesity therapies: a microsimulation and threshold analyses. Gut. 2023 Nov 24;72(12):2250-2259. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330437. PMID: 37524445.
- Launches and prices of Novo Nordisk’s weight-loss drug Wegovy | Reuters [Internet]. [cited 28 Feb 2024]. Available from: https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/launches-novo-nordisks-weight-loss-drug-wegovy-2023-09-04/
- Salinari A, Machì M, Armas Diaz Y, Cianciosi D, Qi Z, Yang B, Ferreiro Cotorruelo MS, Villar SG, Dzul Lopez LA, Battino M, et al. The Application of Digital Technologies and Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: An Overview on Nutrition Assessment. Diseases. 2023; 11(3):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030097
Table of Contents
